Architecture
The Data Sharing Framework implements a distributed business process engine based on the BPMN 2.0 and FHIR R4 standards. Every participating organisation (e.g. ORG. A) runs a FHIR endpoint accessible by other sites and a business process engine (BPE) in the local secured network. Once the DSF has been installed in an organisation, it can be used for multiple use cases.
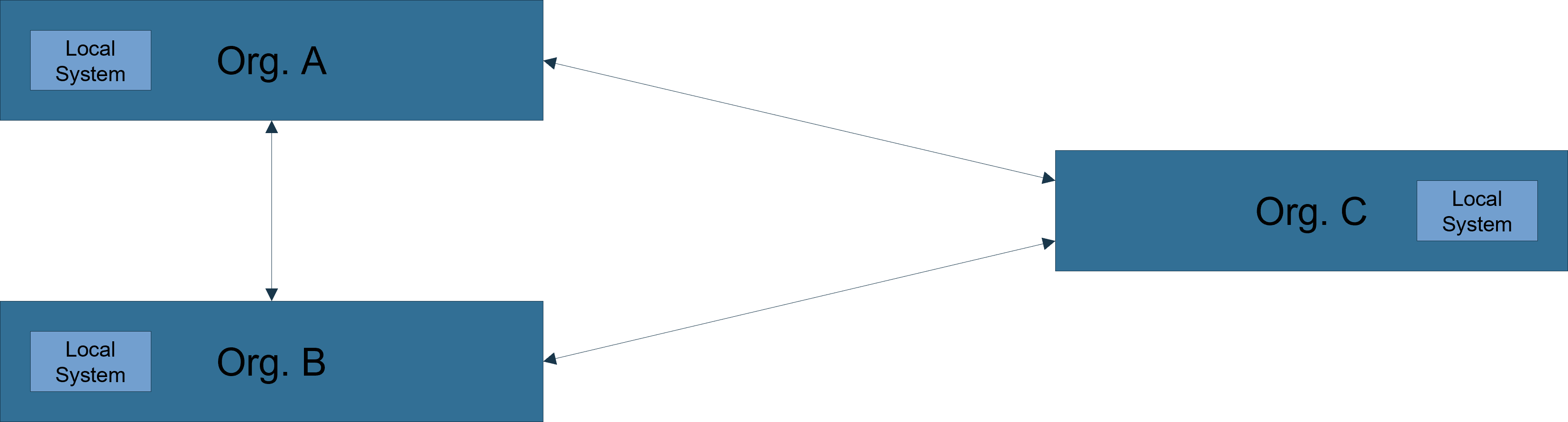

The following architecture diagram also shows three organisations, each of which has installed the DSF. The FHIR endpoint (green) is located in a demilitarised zone (DMZ) and is accessible from outside for communication with other organisations. It can be compared to a mailbox. The Business Process Engine (BPE - blue) is located in the intranet of an organisation and is responsible for the execution of processes. The metaphor: control centre helps here.


DSF FHIR Server 📫
As mentioned above, the externally accessible DSF FHIR server acts as a mailbox for communication. This means that an organisation creates a task resource in its DSF and drops the task resource (letters) into the mailbox of another organisation, requesting that something happen. Task resources have been explained in more detail in the section Basics and Standards.
It is important to understand that the DSF FHIR server is not used for persisting medical data.


Business Process Engine (BPE)
The BPE located in the secure internal network executes the processes (BPMN/Java). The BPE is deployed in the internal network and has access to the local systems, such as the organisation's own FHIR server, on which medical data is stored. These FHIR servers are not to be confused with the DSF FHIR server, on which no medical data is persisted.
Different processes can be executed simultaneously. For this, only a new process plugin file has to be added and configured. More about this in the Process Plugins.


The DSF BPE uses websocket (WSS) and webservice (HTTPS) connections to communicate with the DSF FHIR server. FHIR resources are created, read, updated and deleted via HTTP requests against the FHIR webservice API. The FHIR subscription mechanism is used to communicate Task resources with status 'requested' and QuestionnaireResponse resources with status 'completed' to the BPE via websockets. When the BPE starts and before the websocket connections are established, 'requested' Task resources and 'completed' QuestionnaireResponse not seen by the BPE are read via webservice requests.
Flexible Deployment
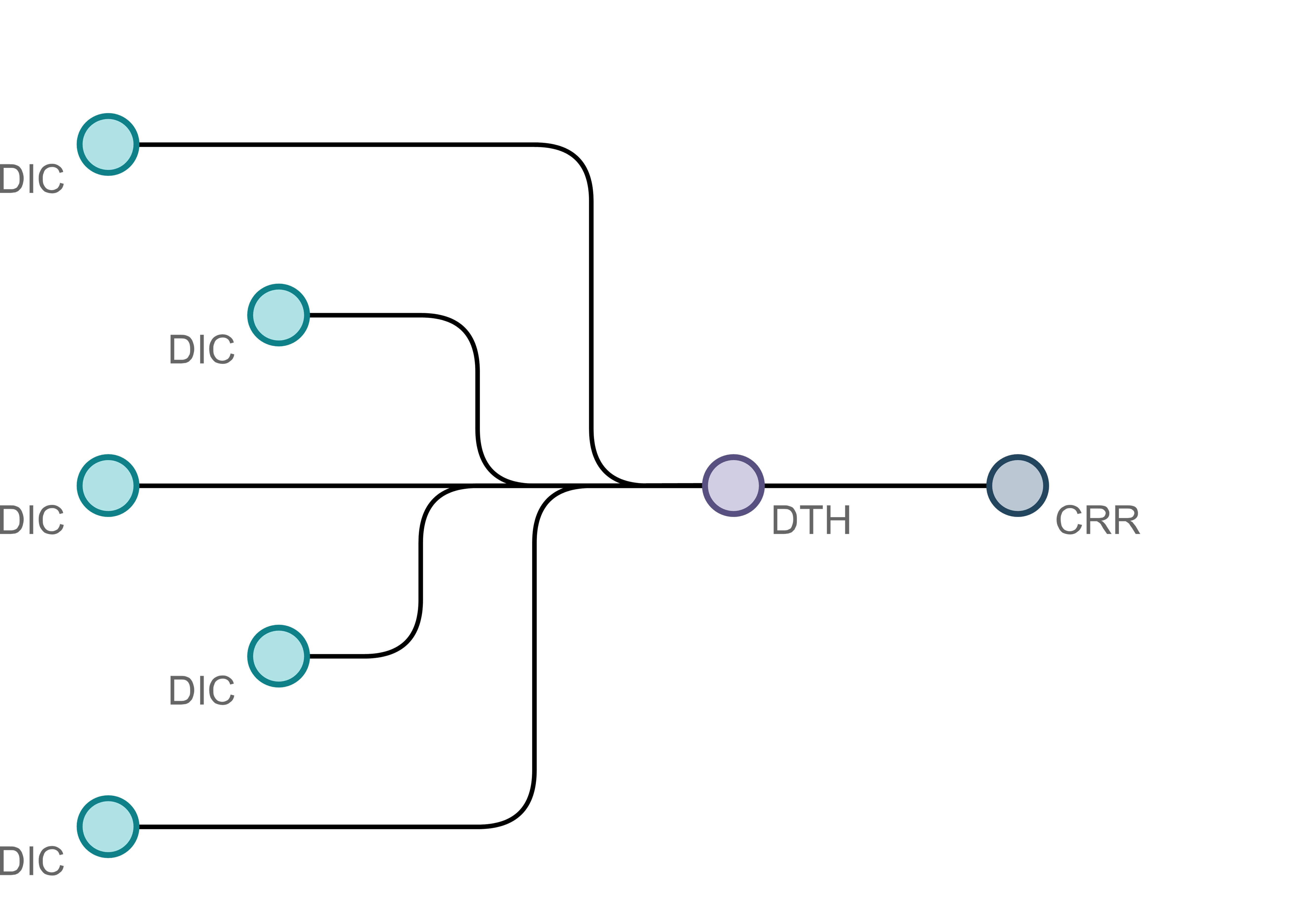
The deployment of the architecture is flexible. The organisations can be deployed as a star schema (left) or as a mesh schema (right). In the Star schema (left), all Data Integration Centres (DIC) are connected to a central node (CRR - Central Research Repository), which transfers the information to all nodes (DIC). For security reasons, a data transfer hub (DTH) is connected upstream, which provides additional security so that the medical data is never transferred together with the authenticating data.
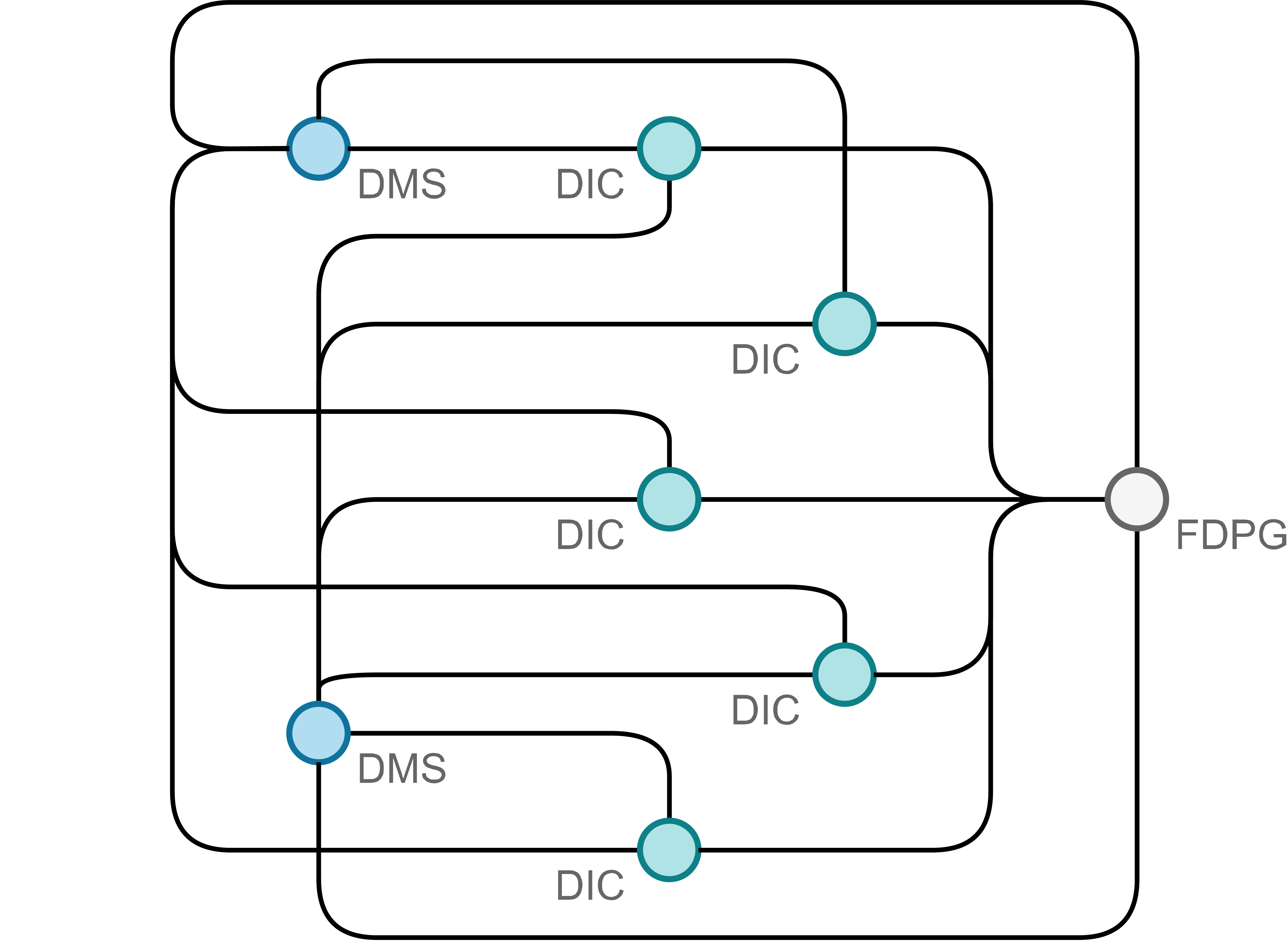
In the mesh scheme (right), the nodes (DIC) are all directly connected to each other and the information is transferred from node to node. Here in the FDPG (Forschungsdatenportal - Research Data Portal), the data can then be accessed for research purposes. More about this here.
Network Setup & Additional Reverse Proxy in external DMZ
You can find more information about the network setup here
